| MANAGEMENT OF HAZARDOUS WASTE |
This indicator shows the amounts of generated hazardous waste, amounts of imported and exported hazardous waste, amount of temporarily stored hazardous waste, as well as treated hazardous waste as a whole.
- The amounts of hazardous waste are presented in tons, cubic meters and share of waste (%).
What is the manner of hazardous waste management, i.e. what is the trend of hazardous waste generation, import and export and the manner of its treatment?
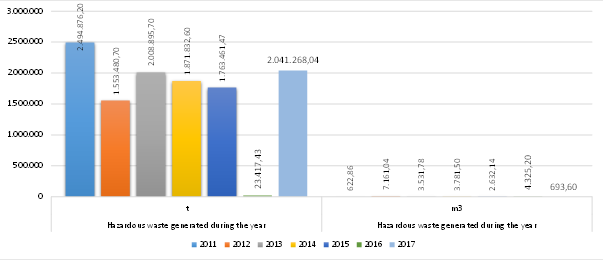
Prevailing manner of hazardous waste management is its disposal by commercial entities that generate it themselves, followed by waste disposal, and then by hazardous waste recovery. As of 2011, the amount of generated hazardous waste has been decreasing gradually, with certain increase noted in 2013 compared to 2012. In 2016 there are huge decrease in the amount of generated hazardous waste as a lack of the annual report of generation of hazardous waste from REK Bitola which generate more than 90% of the hazardous waste in the Republic of Macedonia. Again in 2017 there is increase in generation of hazardous waste.
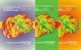
Figure 1. Overview of the total generated hazardous waste presented in tons and cubic meters in the period 2011-2017
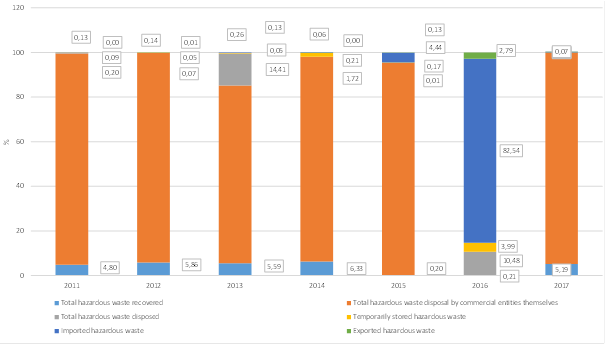
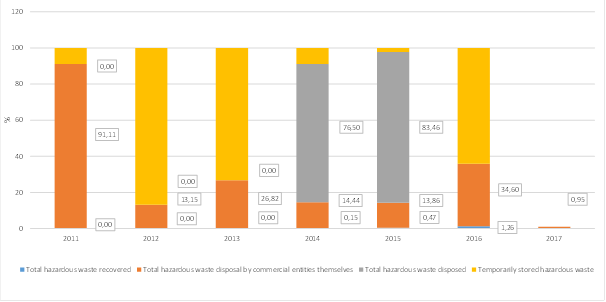
Figure2. Share of the amount of imported and treated hazardous waste presented in tons
Figure3. Share of the amount of imported and treated hazardous waste presented in m3
Data coverage: excel
Source of data: Ministry of Environment and Physical Planning
Prevailing manner of hazardous waste management in the period from 2011 to 2015 was its disposal by commercial entities that generated it themselves and it ranged from 94.92% in 2015 to 79.434% in 2013 as the least favourable manner of waste management with regard to consequences on environment and human health. The rate of hazardous waste recovery was 4.79 % in 2011, 6.31% in 2014, and there was great drop in hazardous waste recovery in 2015 and 2016 amounting 0.2%.
The waste that cannot be treated or disposed appropriately is temporarily stored. Temporarily stored hazardous waste is the waste pending disposal or treatment. Treatment can be carried out in the country of generation or in another country. Uncontrolled transboundary movement of hazardous waste and its disposal or inappropriate handling may cause heavy health problems in people and may contaminate water and soil. Recycling, appropriate incineration and appropriate disposal of hazardous waste in the country of its disposal reduces the demand for hazardous waste transboundary movement and thus reduces the risk for human health and environment. In certain cases, international transport of hazardous waste is necessary and justified in terms of the waste proper disposal and treatment with no consequences for human health and environment, and such is its reuse as secondary raw material or for energy production.
Import of hazardous waste in the Republic of Macedonia increased as of 2012 up to 2015 and 2016 ranging from 0.052% to 4.43% for 2015 and 82.54%. Export of hazardous waste ranged from 0.0025% for 2014 to 0.125% for 2015 and 2.79 for 2016. Data on generated, imported, exported and disposed hazardous waste helps to control and monitor its movement and removal.
Certain types of hazardous waste are grouped according the main economic activities based on the National Classification of Activities NCA Rev. 2 harmonized with the International Standards for Industrial Classification of All economic activities (ISIC).Types of hazardous waste are determined by the List of waste types. Appropriate treatment and disposal of waste are in accordance with definitions and conditions set in the Law on Waste Management. Collection of data is acquired mainly through submission of annual reports on hazardous waste management by commercial entities that generate hazardous waste from 2011 to 2016.
List of relevant policy documents:
Second National Environmental Action Plan of the Republic of Macedonia (2006)
Strategy for Waste Management in the Republic of Macedonia (2008-2020)
National Waste Management Plan (2009-2015) of the Republic of Macedonia
Legalgrounds
- Law on Waste Management (2004)
- National Classification of Activities NCA Rev.2 2006)
- List of waste types (2005)
- Ratified Basel Convention
Establishment of integrated waste management and financially self-sustainable waste management system.
- EUROSTAT
| Code | Title of the indicator | Compliance with CSI/ЕЕА or other indicators | Classification by DPSIR | Тype | Linkage with area | Frequency of publication | |
| MK NI 056 | Management of hazardous waste | UNECE | I-2: Management of hazardous waste | P
R |
А |
|
2 – year |