| EXCEEDANCE OF AIR QUALITY LIMIT VALUES IN URBAN AREAS – SO2 |
The indicator shows the portion of urban population potentially exposed at ambient air concentrations of pollutants in excess of the limit value set for human health protection.
Urban population taken into account is actually the total number of inhabitants living in cities with at least one monitoring station. These cities include the capital and other major cities of the Republic of Macedonia. The number of inhabitants is based on the last census carried out by the State Statistical Office in 2002.
Exceedance of air quality limit values occurs when the concentration of air pollutants exceeds the limit values for SO2, PM10, NO2 and the target values for O3 as specified in the Decree on the limit values of levels and types of polluting substances in ambient air and on the alert thresholds, deadlines for the limit values achievement, margins of limit value tolerance, target values and long-term ozone targets (Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia No. 50/05, 4/2013), wherein the requirements of the Directive on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air in Europe 2008/50 EC and Heavy Metals Directive 2004/107/EC have been transposed. Where there are multiple limit values (see section on Policy Targets), the indicator uses the most stringent case:
- Sulphur dioxide (SO2): the daily mean limit value
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2): the annual limit value
- Particulate matter of a size up to 10 micrometer (PM10): the daily mean limit value
- Ozone (O3 ): the short term objective
The percentage of urban population potentially exposed at ambient air concentrations of sulphur dioxide (SO2), particulate matter sized up to 10 micrometer (PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and ozone (O3) above limit values set for human health protection. Ambient air concentrations of sulphur dioxide (SO2), particulate matter sized up to 10 micrometer (PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and ozone (O3) are expressed in microgram/m3(µg/m3).
What progress has been achieved in reducing the concentrations of pollutants in urban areas in order to achieve the limit values for SO2 in the Decree?
No excess of mean daily concentrations of sulphur dioxide was recorded in the period from 2004 to 2017, i.e. the population was not exposed at sulphur dioxide concentrations above limit value, except in 2006 when out of the allowed 3 days, exceedance of the limit value was recorded in the course of 8 days in Skopje, which was not seen as significant problem.
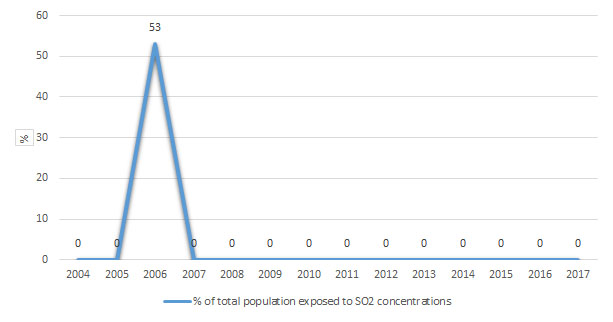
Diagram 1: Percentage of urban population exposed at air pollution in areas where concentrations of pollutants are in excess of limit/target values
Diagram 2: Percentage of urban population exposed at concentrations ofSO2 above the daily mean limit value expressed as number of days in the course of a calendar year
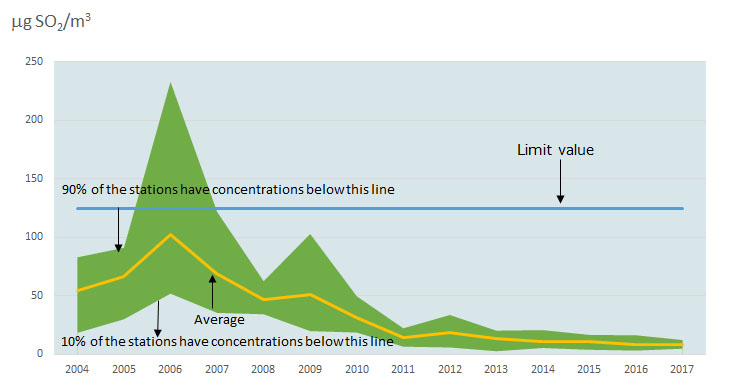
Diagram 3: 4th highest average mean daily concentration of SO2
Data coverage: excel
Source: Ministry of Environment and Physical Planning (https://arhiva.moepp.gov.mk/?lang=en)
Sulphur dioxide in the air most frequently originates from major thermal power plants, as well as from small and medium size boilers for coal combustion in urban environments. The main anthropogenic sources include coal and oil combustion. This pollutant is also released in the air from industrial processes (production of cellulose and paper, sulphuric acid, lead and zinc ores smelting).
In the period 2004 to 2017, there have been no concentrations above the daily mean limit value for sulphur dioxide, i.e. population was not exposed at sulphur dioxide concentrations above the limit value, except in 2006 when out of the allowed 3 days, exceedance of the limit value was recorded in the course of 8 days in Skopje, which was not seen as significant problem.
In 2006, 53% of the population was exposed at sulphur dioxide concentration above125 mg/m3for more than 6 days in the course of the year. In 2005 and 2007, there was higher percentage (around 50%) of the population exposed at sulphur dioxide concentration above 125 mg/m3 for 1 to 3 days in the course of the year, while in 2008 and 2009, this percentage of population exposure was very low (3%).
- Methodology for the indicator calculation
For each measuring station located in urban environment, the number of days with mean daily concentration higher than the limit value (daily mean value of 125 µg/m3) is calculated from the available hourly data. Selected urban stations include stations of the following types: stations measuring traffic pollution, stations measuring industrial pollution and urban background stations. The number of days with excess in a city is obtained by averaging the results of all stations located in that city.
Uncertainty
- Methodological uncertainty and data uncertainty
In general, data is not representative for all urban environments in the Republic of Macedonia. Compared to the methodology of the European Environmental Agency, where the calculation of the indicator is based only on data produced by the urban background stations, in our calculations we used data from all measuring stations located in urban environments. Also, due to the minimum number of monitoring stations, the calculation of the indicator also took into account the stations where data coverage is below 75% per calendar year. We can also point out as uncertainty in the indicator calculation the fact that the number of inhabitants in cities is based on the census of the population conducted by the State Statistical Office in 2002, instead of estimated number of population for each year.
List of relevant policy documents
The National Plan for Air Protection presents the state of air quality, defines the measures for ambient air quality protection and improvement in the Republic of Macedonia and all relevant institutions responsible for their implementation within 5 year period, namely from 2013 to 2018 (Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia no.170/2012).
Legal grounds
The Law on Ambient Air Quality was adopted in August 2004 and later amended on several occasions in line with the requirements of the relevant EU legislation (Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia Nos. 67/2004, 92/2007, 83/2009, 35/2010, 47/2011, 59/2012, 163/13, 10/15 and 146/15) and it is framework law in the area of air. The main goals of this Law are: avoidance, prevention and reduction of harmful effects on human health and environment as a whole, prevention and reduction of pollution resulting in climate change, as well as provision of the relevant information on the quality of ambient air. This Law establishes the legal grounds for adoption of a number of bylaws in line with the requirements of the relevant Acquis Communitaire. So far, 12 bylaws have been adopted. Calculations for this indicator are based on the provisions of the Decree on the limit values of levels and types of polluting substances in ambient air and on the alert thresholds, deadlines for the limit values achievement, margins of limit value tolerance, target values and long-term ozone targets (Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia No. 50/05, 4/2013 and 183/2017).
The Decree on the limit values of levels and types of polluting substances in ambient air and on the alert thresholds, deadlines for the limit values achievement, margins of limit value tolerance, target values and long-term targets, defines the limit values for SO2, PM10, NO2 and target values for O3.
Limit values for concentrations of sulphur dioxide in ambient air
In accordance with the said Decree, two limit values are specified for sulphur dioxide for the purpose of human health protection.
- Mean daily limit value of 125 µg/m3 which shall not be exceeded by more than three times during one calendar year
- Hourly limit value of 350 µg/m3, which shall not be exceeded by more than 24 times during one calendar year.
European Environmental Agency
- Air quality data exchange in accordance with implementing Decision containing the rules of Directives 2004/10/EC and 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning reciprocal exchange of information I reporting on ambient air quality (Decision 2011/850/EC).
| Code | Title of the indicator | Compliance with CSI ЕЕА or other indicators | Classification by DPSIR | Type | Linkage with area | Frequency of publication | |
| MKNI 004 | Exceedance of air quality limit values in urban areas | CSI 004 | Exceedance of air quality limit values in urban areas | S | А | air
Air quality |
annual |