| TOTAL ENERGY INTENSITY |
Total energy intensity is the ratio between the total energy demand (or total energy consumption) and the Gross Domestic Product.
The total energy consumption is calculated as the sum of the total energy demand from solid fuels, oil, natural gas and renewable sources.
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is converted by the Price Adjusted Rate of Exchange (PARE) method, applying the OUN Methodology (2000 database).
The total energy demanded (or total energy consumption) is expressed in thousand tonnes oil equivalent, and Gross Domestic Product in million EUR.
The indicator “Total energy intensity” is expressed in kilograms oil equivalent per 1000 EUR (kgoe/1000 EUR).
The indicator is also calculated in indexes with 2000 as base year (2000=100).
- million EUR
- thousand tonnes oil equivalent (ktoe)
- kilograms oil equivalent (kgoe)
- indexes (2000=100)
What will be the dynamics of strategic targets implementation and achievement?
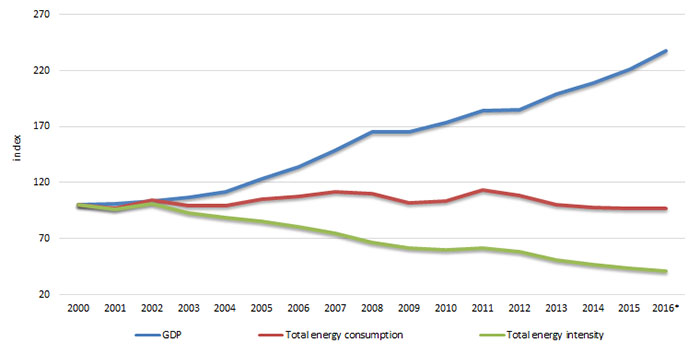
The trend in Energy intensity in the Republic of Macedonia recorded a decline by 59.1% in 2016compared to 2000, mainly due to the trend of GDP growth of 137.4% in the same year. The largest drop in the energy intensity, compared to the previous year, from 13.68%, was registered in 2013 in comparison to 2012, and the largest increase by 5.51% in 2002 compared to 2001.
Figure 1. Total energy intensity
Data coverage: excel
Source: State Statistical Office, http://www.stat.gov.mk/Default_en.aspx
There is a constant change in the trend of total energy intensity from 2000 to 2016, with an average rate of decline of 5.3%. In 2016, compared to 2000, a decline in energy intensity of 59.1% was noted as a result of a 137.4% increase of GDP in the same year. The larest drop in the energy intensity compared to the previous year, from 68%, is noted in 2013 compared to 2012, and the highest increase of 5.5% in 2002 compared to 2001.
A favorable trend of a decrease in energy intensity can be noted from the time series.
A comparative analysis of energy consumption in relation to GDP, a so called indicator of energy intensity, shows that the Republic of Macedonia belongs to the group of countries with relatively high energy consumption, due to the high energy intensification of the capacities that carry the economic growth. Also, due to the long term treatment of the price of electricity as a social category, the residential sector uses a considerable amount of electricity for heating.
- Methodology for the indicator calculation
Statisticalmethodologyforcalculation:
- Regulation on Energy Statistics of the European Parliament and of the Council (Regulation no.1099/2008),
- „Energy Statistics Methodology Eurostat F4, 1998″
- National classification of activities NCA Rev.2 (Official Gazette of the Republic of Macedonia no. 147/2008).
List of relevant policy documents:
- Strategy for Energy Efficiency Promotion in the Republic of Macedonia by 2020[1]
- Strategy for Energy Development in the Republic of Maceodnia by 2030[2]
Legal grounds
Law on Energy; Energy Balance of the Republic of Macedonia – annual planning document defining the demands for energy and the possibility for their supply (Article 16 of the Law on Energy).
[1]http://www.konkurentnost.mk/StrateskiDokumenti/StrategijazaunapreduvanjenaEERMdo2020godina.pdf [2]http://www.build.mk/docs/users/cloverstack/Strategija%20za%20razvoj%20na%20energetikata%202008-2020%20so%20vizija%20do%202030.pdf
Target to be achieved in EU is spending tonnes oil equivalent per 1.000 US$ GDP, while the target in the Republic of Macedonia is 0,75 tonnes oil equivalent. The implementation of measures under the Strategy for Energy Efficiency Promotion, this should drop down to 0,45 to 0,49 intо 2020.
- Eurostat
- ECE/UN
- IEA/OECD
| Code | Title of the indicator | Compliance with CSI/ЕЕА or other indicators | Classification by DPSIR | Type | Linkage with area | Frequency of publication | |
| MKNI 028 | Total energy intensity | CSI 028
EE 23 |
Total energy intensity | R | B |
|
annualy |