| LAND TAKE |
Changes in and current status of agriculture, forest and other semi-natural land taken by urban and other artificial land development. It includes areas sealed by construction and urban infrastructure as well as urban green areas and sport and leisure facilities. The main drivers of land take are grouped in processes resulting in the extension of:
- housing, services and recreation,,
- industrial and commercial sites,
- transport networks & infrastructures,
- mines,quarries and waste dumpsites.
Units of measurement for changes and current status recording and mapping are hectares. For data presentation, the unit in km2 can be used as well.
Results are presented as:
- current status of land cover based on the nomenclature adopted at European level, at five-year intervals;
- changes in land cover, at five-year intervals, presented in % of the total area of the country and % of the various land cover types.
Note: Particular attention is paid to areas changing as a result of urban systems extension leading to negative impact on the environment.
How much and in what proportions is agricultural, forest and other semi-natural and natural land being taken for urban and other artificial land development?
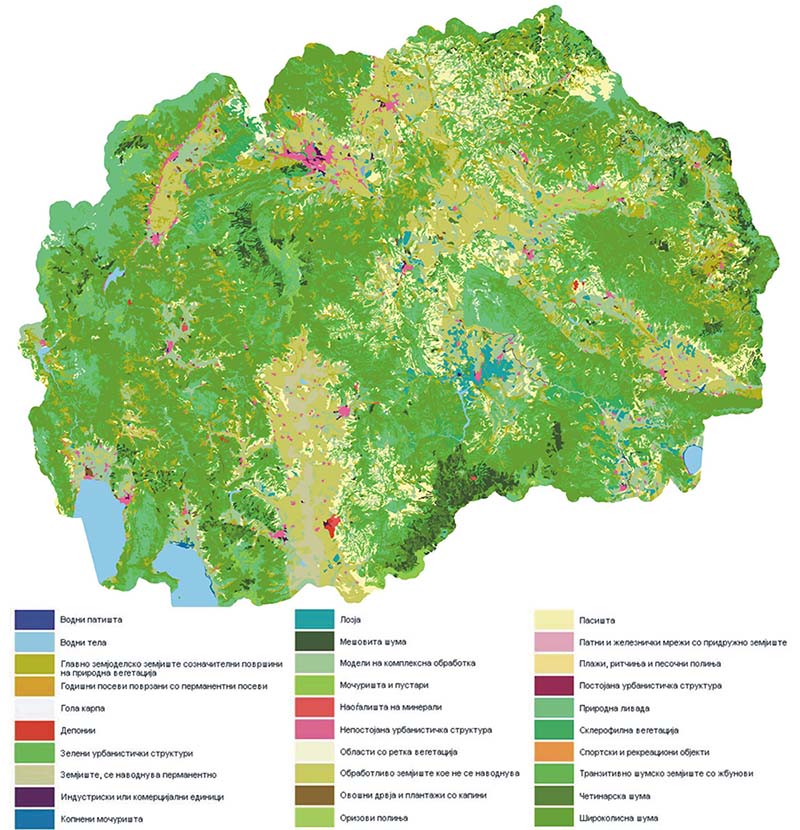
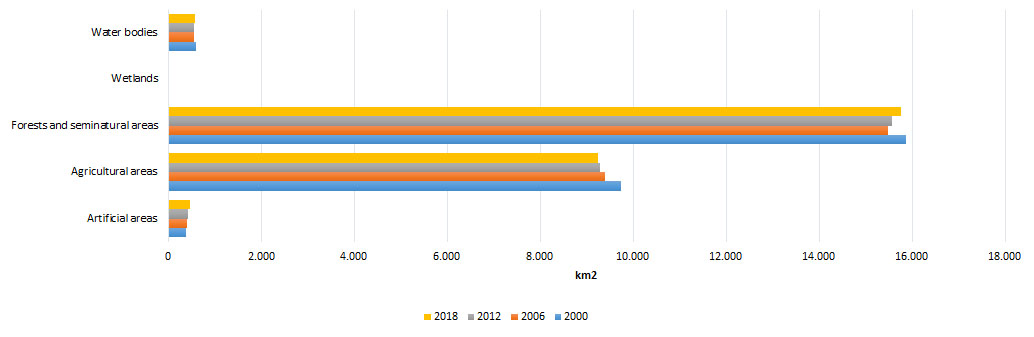
Based on the CORINE Land COVER methodology, the largest portion of the land in the Republic of Macedonia is under forest and semi-natural areas, covering 15,770 km2 or 61.3% of the total area. The category of agricultural land area covers 9,248 km2or36% of the total area, the category of water bodies covers 577 km2or 2.2% of the total area, the category of artificial areas covers 464km2 or 1.8% of the total area, and the smallest area of 22km2 or 0.1% of the total area is wetlands (Figure 1).
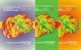
Map 1. CORINE Land COVER 2018
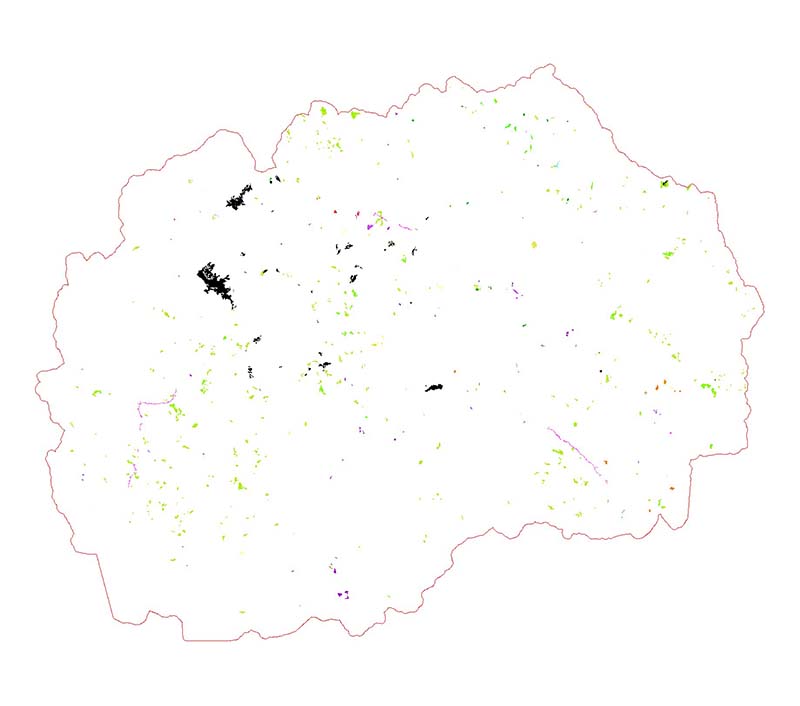
Map 2. CORINE LandCover overall changes 2012-2018
Figure 1. Area of individual areas by CORINE nomenclature and share in the total territory of the country
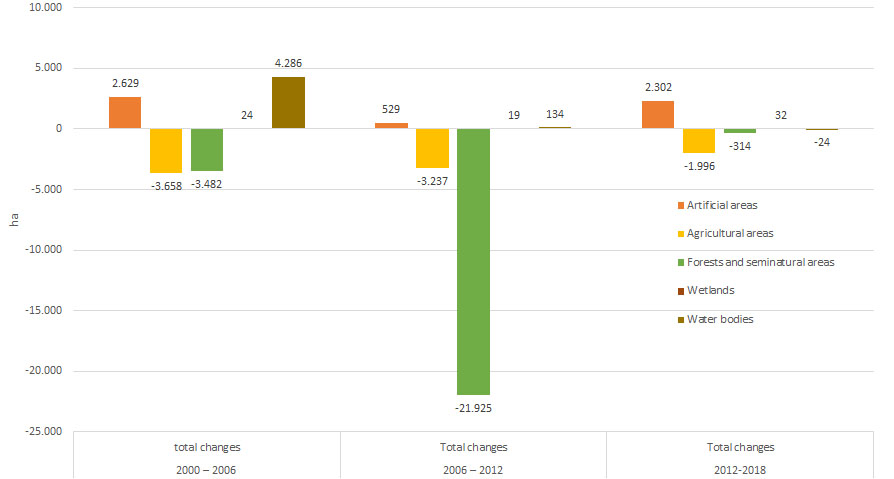
Figure 2. CORINE level 1 total changes (in hectares)
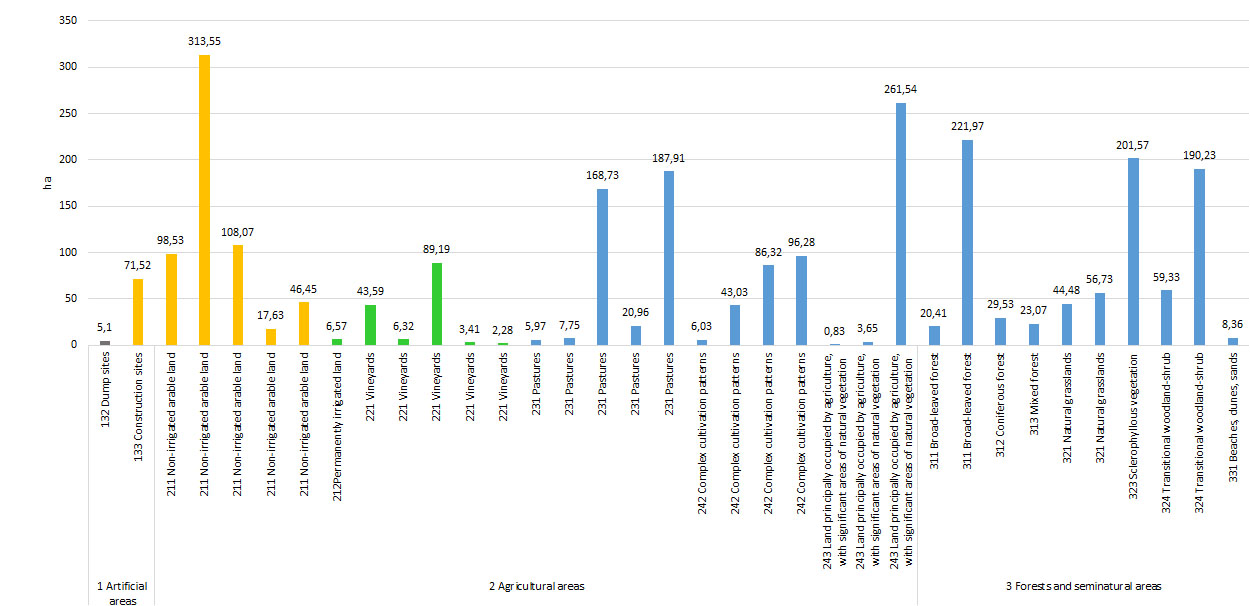
Figure 3. Relative contribution of land-cover categories to uptake by urban and other artificial land development (2012-2018)
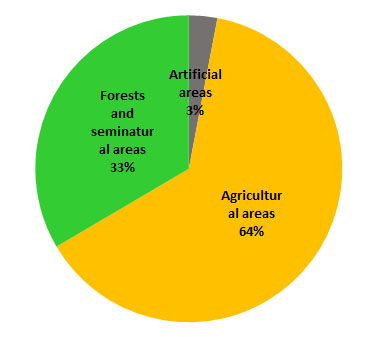
Figure 4. Relative contribution of level 1 categories transformed into urban and other artificial land development (2012-2018)
Data coverage: excel
Source: CORINE Land Cover
Owing to characteristics of land cover of the territory of the Republic of Macedonia, out of 44 possible classifications under the CORINE LandCover Nomenclature, 33 classifications have been identified up to the third level of the Nomenclature.
As a result of CORINE LandCover Project, as illustrated on Figure 2, the greatest overall changes in the period 2012 to 2018, were recorded for the growth of artificial land area and reduction in agricultural land area and forest and semi-natural areas.
CORINE LandCover changes between 2012 and 2018 cover territory of around 28,985 ha which is around 1.13% of the total territory of the country.
Table 1 shows the absolute values of changes. It is evident that the most of the changes occurred in artificial areas, where new 2,302 ha has been generated. Other negative trend is in the decreasing of the area of agricultural land for 1,996 ha. Other changes are minimal, from decreasing water bodies for 24 ha, increasing wetlands for 32 ha to decreasing total area of forest and semi-natural areas for 288 ha.
Table1. Absolute values for changes (2012-2018)
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Into | 2,666 | 1,971 | 24,207 | 32 | 110 |
| From | 364 | 3,967 | 24,494 | 0 | 134 |
| Absolute | 2,302 | -1,996 | -288 | 32 | -24 |
- Methodology for the indicator calculation
The assessment of CORINE LandCover in 2000, 2006, 2012 and 2018 was based on data from satellite images.
Owing to characteristics of the land cover of the Republic of Macedonia, out of the possible 44 classifications, 33 were identified.
The substance of the process is photo-interpretation of satellite images consisting of:
- Delineation of boundaries of areas representing unique land area units at images with “false” colours;
- Application of interpretation keys, supporting documentation and satellite/aeroplane images for marking with identification number – class in nomenclature;
- Extrapolation of this marking and identification of all segments of the image exhibiting similar characteristics: colour, structure and composition.
Technical Guideline for CORINE Land Cover development was prepared by the European Environmental Agency.
Legal grounds
Under the Law on Environment, every citizen is entitled to have an access to environmental state information. This indicator provides not only data on the state of the environment (land cover), but it also facilitates uniform access thereto, both at national and European levels.
Based on the Law on Land Survey and Registration, by means of regular land survey information is provided on the types of land cover. Although these parameters do not correspond with the CORINEland cover nomenclature, there is a possibility for unique integration of land cover elements.
Law on Urban and Spatial Planning.
Tracking the changes in land cover and mapping of current status. Changes are monitored over five-year intervals. Methodology and nomenclature have been additionally harmonized at European level, thus enabling integrated monitoring of changes at regional and European levels.
- EEA
| Code | Title of the indicator | Compliance with CSI/ЕЕА or other indicators | Classification by DPSIR | Тype | Linkage with area | Frequency of publication | |
| MKNI 014 | Land take | CSI 014 | Land take | P | A |
|
10 – annually |