| FINAL MUNICIPAL WASTE MANAGEMENT |
This indicator shows the final management of the overall amount of municipal waste through the processes of:
– Incineration (with and without energy recovery)
– Landfilling (controlled or uncontrolled landfills)
– Composting
– Reuse or recycling
– Other manner of management.
- Tons/year, percentage (%).
In which way or through which processes the final waste management is performed?
Waste landfilling on controlled landfills is the prevailing process in the final waste management in the Republic of Macedonia, followed by waste disposal on uncontrolled landfills. The processes of composting, reuse, recycling of municipal waste, as well as waste incineration with energy recovery are almost not represented in the country.
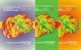
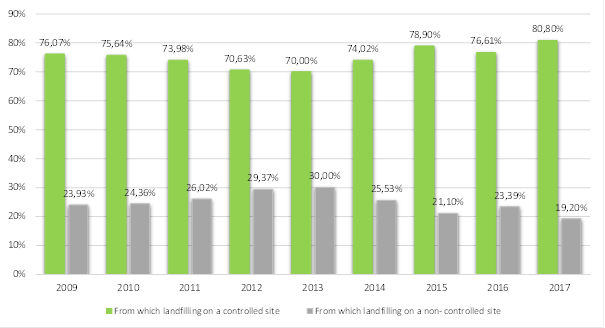
Figure 1. Overview of % of municipal waste landfilling on controlled and uncontrolled landfills
Data coverage: excel
Source of data: State Statistical Office, http://www.stat.gov.mk/Default_en.aspx
The way in which the waste is managed in the country has great impact on environment, economy and human health and wellbeing. Adequate waste management assumes that the Government is aware if the risks of waste for human health and environment and it supports and promotes appropriate measures to prevent waste generation or reduce it, as well as to manage it properly. Reduction in the amount of generated waste, as well as reuse and recycling of generated waste are ecologically the most favourable processes of waste management, as it also accomplishes reduction in raw materials and resources extraction. Another option of management of the waste that cannot be reused or recycled is incineration with energy recovery. The last option in waste management is its disposal in landfills and technically appropriately managed and controlled landfills are recommended for this purpose.
The two most represented processes of waste management, namely disposal of waste on controlled and uncontrolled landfills, are rather unfavourable for the environment, health of people and animals, as well as economy. Waste disposal on controlled landfills in the period 2009 to 2016ranged from 70.0% to 78.9%, while disposal of waste on uncontrolled landfillswas in the range between 21.1% in 2015and30.0% in2013. All this indicates pollution of the environment and loss of natural resources. Absence of the processes of reuse, recycling, composting and incineration of waste with energy recovery reflects lack of recognition of the waste as resource and lack recovery of energy and matter contained in the waste.
Types of hazardous waste are determined by the List of waste types. Appropriate treatment and disposal of waste are in accordance with definitions and conditions set in the Law on Waste Management. Collection of data is acquired mainly through surveys, estimates, and administrative data. Reports are in a form of releases of the State Statistical Office (2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016).
List of relevant policy documents:
Second National Environmental Action Plan of the Republic of Macedonia (2006)
Strategy for Waste Management in the Republic of Macedonia (2008-2020)
National Waste Management Plan (2009-2015) of the Republic of Macedonia
Legal grounds
- Law on Waste Management (2004)
- List of waste types (2005)
Establishment of integrated waste management and financially self-sustainable waste management system.
- EUROSTAT
| Code | Title of the indicator | Compliance with CSI/ЕЕА or other indicators | Classification by DPSIR | Тype | Linkage with area | Frequency of publication | |
| MK NI 057 | Final waste management | UNECE | I4a – Final waste disposal: Management of municipal waste | I | А |
|
2 – years |