| TOURISM INTENSITY IN THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA
3 National tourists intensity |
The indicator shows the total number of overnights of national tourists by years at country level and by statistical regions and average stay of tourists.
- Number
Does the number of nationaltourists, overnights and average stay have development dimension?
With regard to national tourist visits, the overall number of tourists during the analyzed period has had falling trend of 9.9%. Furthermore, it is obvious that the accomplished overnights parallel tourist visits and have had falling trend of 23.7% during the analyzed period. The average stay of national tourists of 4.75 days in 2000 dropped to 4.02days in 2017.
By statistical regions, the highest number and overnights of national tourists were recorded in Southwestern region and the lowest in Northeastern region.
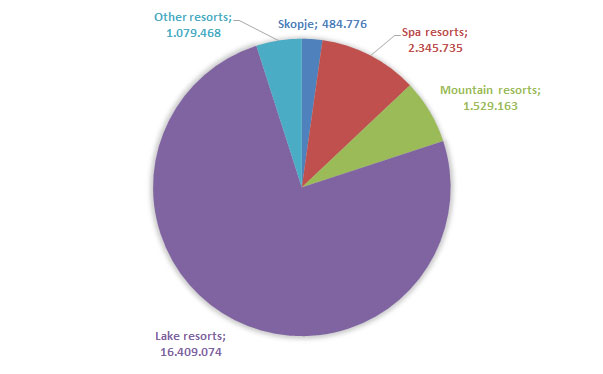
With regard to national tourist arrivals by types of resorts, the highest number of national tourists was recorded in lake resorts with 2.887.029tourists and the lowest in Skopje with 317.486tourists. As for overnights of national tourists by types of resorts, the highest number of overnights was recorded in lake resorts with 16.409.074overnights and the lowest number in Skopje with 484.776overnights.
Figure 1. Total number of national tourists and number of overnights
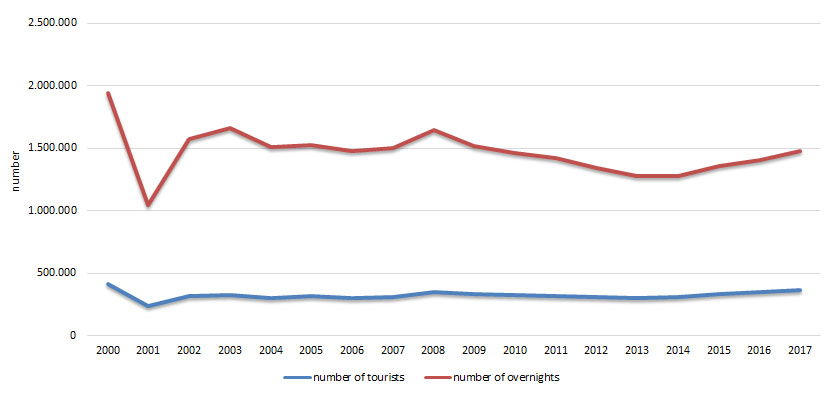 Figure 2. Average stay of national tourists
Figure 2. Average stay of national tourists
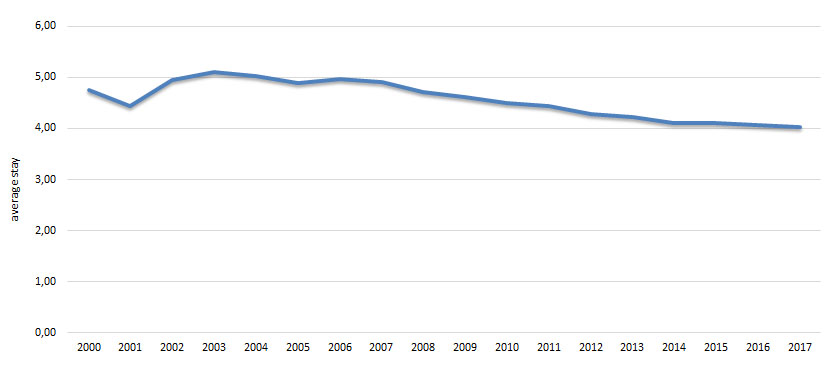 Figure 3. Number of national tourists and number of overnights by statistical regions
Figure 3. Number of national tourists and number of overnights by statistical regions
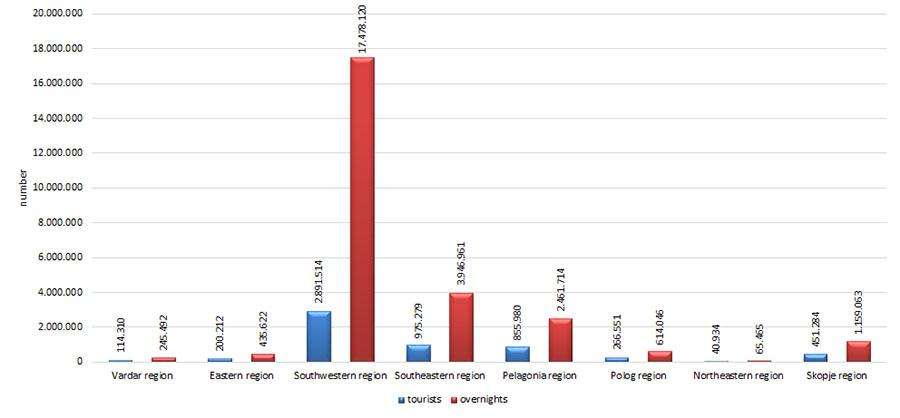 Figure 4. Arrivals of national tourists by types of resorts in the period 2003 to 2016
Figure 4. Arrivals of national tourists by types of resorts in the period 2003 to 2016
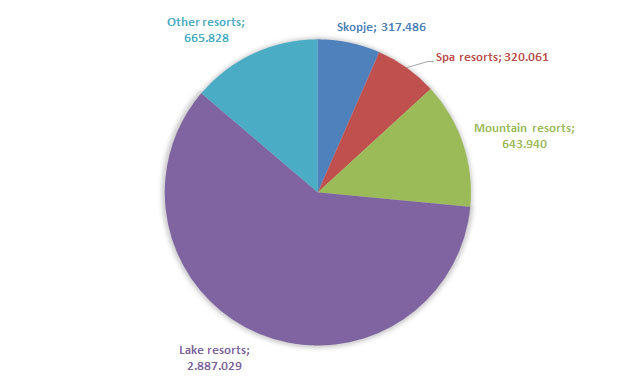 Figure 5. Overnights of national tourists by types of resorts in the period from 2003 to 2016
Figure 5. Overnights of national tourists by types of resorts in the period from 2003 to 2016
Data coverage: excel
Data source: State Statistical Office, http://www.stat.gov.mk/Default_en.aspx
The number of national tourists has had falling trend of 9.9%; namely, the number of national tourists in 2000 was the highest, and it was the lowest in 2001. Similar characteristics have been observed with overnights accomplished by national tourists, i.e. the highest number of overnights was accomplished in 2000 and the lowest number of overnights in 2001. Also, the results reflect these relations with regard to average stay, showing significant fall in the number of overnights from 2007 to 2016. The shortest average stay of 4.02 days was recorded in 2017 and the longest one in 2003 amounting 5.1 days.
Southwestern region holds prevalence with regard to national tourists distribution, which can be assessed both as favourable aspect and uneven distribution. Observation of these indicators should indicate the extent to which the number of national tourists will increase in other regions as a result of the promotion of environmental elements in touristic offer on the national tourist market.
Furthermore, we may conclude that accomplished overnights follow tourist visits as a result of the attractiveness of the environment and thus the highest number of overnights is recorded in Southwestern region. Observation of overnights will show the extent to which regions will improve attractive base as factor in accomplishing higher number of overnights.
With regard to national tourist arrivals by types of arrivals, the highest share in the overall number of tourists was recorded in lake resorts with 59.75%, followed by other resorts with 13.77%, mountain resorts with a share of 13.32%, spa resorts with a share of 6.62% and the lowest share was recorded in Skopje with 6.57% in the total number of tourists.
With regard to overnights of national tourists by types of resorts, the highest share in the total number of overnights was recorded in lake resorts with 75%, followed by spa resorts with 10.74%, mountain resorts with a share of 7%, other resorts with share of 4.94% and Skopje noted the lowest share with 2.22% in the total number of overnights.
- Methodology for the indicator calculation
The trend in tourism development through dynamics and intensity of tourist industry.
The scale and the intensity, as well as the share of individual countries in the total number of foreign tourists arrivals and overnights, national tourists arrivals and overnights, regional distribution and average number of days of stay.
List of relevant policy documents
- National Strategy for Tourism Development 2009 – 2013 (revised in 2015)
- National Environmental Action Plan – 2 – in Section 4.2.6. Tourism, describes the main challenge for sustainable tourism development, implementation of economic potential with minimum possible impact on the environment.
- Spatial Plan of the Republic of Macedonia – in its Chapter 5.4. “Tourism development and organization of tourist areas”, defines the status, objectives and planning determinations for tourism development.
- National Strategy for Sustainable Development of the Republic of Macedonia – in the section on tourism, presents the directions for sustainable development of tourism, within short, medium, and long-term frames, up to 2030.
- Strategy for Biological Diversity Protection in the Republic of Macedonia with Action Plan – under measure C.5 “Stimulation of traditional use of biological diversity and eco-tourism”, defines the action for identification of sites suitable for eco-tourism.
Legal grounds
The Law on Tourist Activity specifies the conditions and the manner of performing tourist activity (Chapter 15 Services in rural, ethno and eco-tourism), Law on Catering Activity.
The Law on Environment, the Law on Nature Protection, the Law on Waste Management, the Law on Ambient Air Quality and the Law on Waters regulate partially the requirements for environmental protection in tourist activity.
- Integration of the principles of sustainable development and environmental considerations in tourist sector
- Identification of areas of priority importance for tourism development
- Encouragement of exchange of best practices between public and private tourist interests
- Protection of natural heritage and biological diversity in tourist destinations
- Adoption and implementation of legislation in the area of tourism to regulate the protection of the environmnet
- Promotion of organic farming, healthy food production and especially traditional production of certain products (e.g. cheese, wine), production of honey, herbs growing, etc.
Promotion of certain types of tourism such as wine tourism, hunting tourism, birds observation tourism, etc.
- Yearly to EUROSTAT
- World Tourist Organization (WTO)
- Annual tourist review of tourism and other services
- Five-year interview of foreign tourists in accommodation establishments
| Code | Title of the indicator | Compliance with CSI ЕЕА or other indicators | Classification by DPSIR | Type | Linkage with area | Frequency of publication | |
| MK NI 047 – 3 | Tourism intensity in the Republic of Macedonia – National tourists intensity | TOUR 12
TOUR 33
|
Tourism
Intensity
Overnights spent in tourism accommodations |
D,P | А | Biological diversity
Nature Policies Waste Water Air Transport Soil |
Yearly
Every five years |