| TOURISM INTENSITY IN THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA
1 International tourist intensity |
The indicator shows the total number of foreign tourists by years at country level and by statistical regions and structure of visitors by country of origin.
- Number
Does the number of tourists in the Republic of Macedonia have development dimension?
With regard to international tourist visits, the total number of foreign tourists during the analyzed period has had development nature or a rising trend of 5.2 times in 2017 compared to 1997.
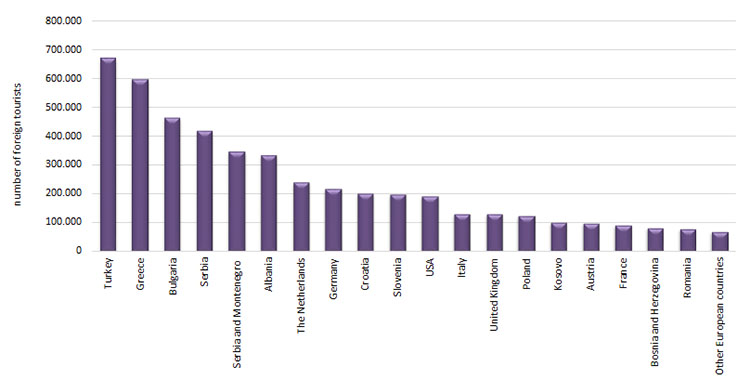
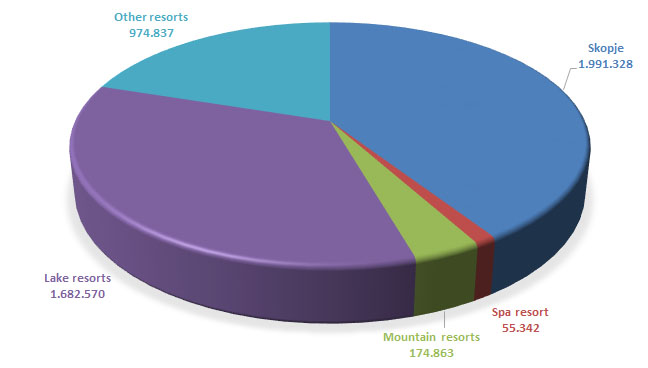
Turkey contributes significantly to the number of tourists in Macedonia with 668.635tourists during the observed period. By statistical regions, the highest number of foreign tourists was recorded in Skopje and Southwestern regions. With regard to foreign tourist arrivals by types of resorts, the highest number of tourists was recorded in Skopje amounting 1.991.328, and the lowest in spa resorts with 55.342 tourists.
Figure 1. Total number of foreign tourists
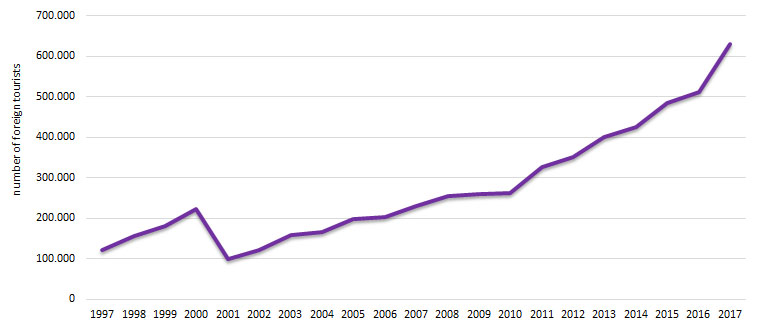 Figure 2. Total number of foreign tourists by country of origin in the reporting period
Figure 2. Total number of foreign tourists by country of origin in the reporting period
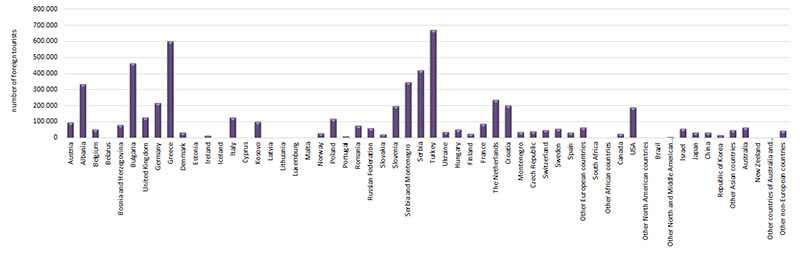 Figure 3. Countries with significant share in the number of foreign tourists
Figure 3. Countries with significant share in the number of foreign tourists
Figure 4. Foreign tourists arrivals by statistical regions
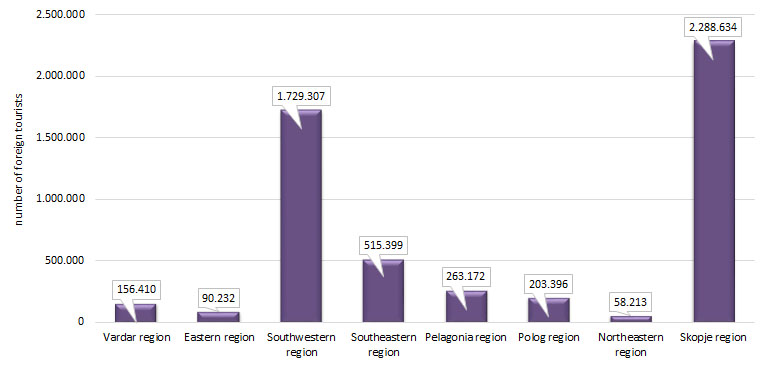 Figure 5. Foreign tourists arrivals by types of resorts in the period from 2003 to 2016
Figure 5. Foreign tourists arrivals by types of resorts in the period from 2003 to 2016
Data coverage: excel
Data source: State Statistical Office, http://www.stat.gov.mk/Default_en.aspx
Data in the Figure indicates that the Republic of Macedonia is visited by a high number of countries. Tourists from Europe, Northern America, Asia and Australia prevail. The structure of visits during the observed period is dominated by tourists from the immediate neighborhood. Leading position among the first twenty counties making significant share in the overall number of foreign tourists belongs to tourists from Greece, Bulgaria, Serbia and Montenegro, Turkey, Albania and Serbia, while the highest number of tourists from among other continents comes from United States of America. Development of attractive and receptive base of the Republic of Macedonia should enable greater presence of tourists from Western European countries having longer tourism tradition and thus higher tourist culture level.Of the Western European countries, a significant rising trend of 23 times, in 2017, compared to 1997, has seen tourists from the Malta. The number of foreign tourists has notable rising trend from 121.337 tourists in 1997 to630.594tourists in2017, which is an increase of 5.2 times. In the reporting period, Turkey has had the highest share with 11.6% or 668.635tourists, while South Africa has had the lowest share with 0.014% or 851tourist of the total number of foreign tourists in Macedonia.
According to regional distribution, Skopje region with2.288.634tourists and Southwestern region with 1.729.309 tourists area leading regional centers for tourists, representing two differentiated regions of different characteristics. Southwestern region is dominated by resource attractiveness, while Skopje region by business activity possibilities. Other regions possess alternative possibilities deriving from different environments and therefore it is important to monitor the intensity of foreign tourist visits with a view to redistribute the intensity of visits.
With reference to foreign tourists arrivals by types of resorts, Skopje has had the highest share in the total number of tourists with 40.81%, followed by lake resorts with 34,49%, other resorts with a share of 19.98%, mountain resorts with a share of 3.58% and the lowest share belongs to spa resorts with 1.13% of the total number of tourists.
- Methodology for the indicator calculation
The data on tourists have been obtained on the basis of the regular monthly reports of catering and other business entities providing services of accommodation to tourists or act as intermediaries in the provision of these services. Guest books kept by business operators as a legal obligation are sources of data.
List of relevant policy documents
- National Strategy for Tourism Development 2009 – 2013
- National Environmental Action Plan – 2 – in Section 4.2.6. Tourism, describes the main challenge for sustainable tourism development, implementation of economic potential with minimum possible impact on the environment.
- Spatial Plan of the Republic of Macedonia – in its Chapter 5.4. “Tourism development and organization of tourist areas”, defines the status, objectives and planning determinations for tourism development.
- National Strategy for Sustainable Development of the Republic of Macedonia – in the section on tourism, presents the directions for sustainable development of tourism, within short, medium, and long-term frames, up to 2030.
- Strategy for Biological Diversity Protection in the Republic of Macedonia with Action Plan – under measure C.5 “Stimulation of traditional use of biological diversity and eco-tourism”, defines the action for identification of sites suitable for eco-tourism.
Legal grounds
The Law on Tourist Activity specifies the conditions and the manner of performing tourist activity (Chapter 15 Services in rural, ethno and eco-tourism), Law on Catering Activity.
The Law on Environment, the Law on Nature Protection, the Law on Waste Management, the Law on Ambient Air Quality and the Law on Waters regulate partially the requirements for environmental protection in tourist activity.
- Integration of the principles of sustainable development and environmental considerations in tourist sector
- Identification of areas of priority importance for tourism development
- Encouragement of exchange of best practices between public and private tourist interests
- Protection of natural heritage and biological diversity in tourist resorts
- Adoption and implementation of legislation in the area of tourism to regulate the protection of the environmnet
- Promotion of organic farming, healthy food production and especially traditional production of certain products (e.g. cheese, wine), production of honey, herbs growing, etc.
Promotion of certain types of tourism such as wine tourism, hunting tourism, birds observation tourism, etc.
- Yearly to EUROSTAT
- World Tourist Organization (WTO)
- Annual tourist review of tourism and other services
- Five-year interview of foreign tourists in accommodation establishments
| Code | Title of the indicator | Compliance with CSI ЕЕА or other indicators | Classification by DPSIR | Type | Linkage with area | Frequency of publication | |
| МК NI 047 – 1 | Tourism intensity in the Republic of Macedonia | TOUR 12 | Tourism
intensity |
D,P | А | Biological diversity
Nature Policies Waste Water Air Transport Soil |
Yearly
Every five years |